Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Train, convert and predict with ONNX Runtime#
This example demonstrates an end to end scenario starting with the training of a machine learned model to its use in its converted from.
Train a logistic regression#
The first step consists in retrieving the iris dataset.
Then we fit a model.
We compute the prediction on the test set and we show the confusion matrix.
[[10 0 0]
[ 0 14 0]
[ 0 0 14]]
Conversion to ONNX format#
We use module sklearn-onnx to convert the model into ONNX format.
from skl2onnx import convert_sklearn # noqa: E402
from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType # noqa: E402
initial_type = [("float_input", FloatTensorType([None, 4]))]
onx = convert_sklearn(clr, initial_types=initial_type)
with open("logreg_iris.onnx", "wb") as f:
f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
We load the model with ONNX Runtime and look at its input and output.
import onnxruntime as rt # noqa: E402
sess = rt.InferenceSession("logreg_iris.onnx", providers=rt.get_available_providers())
print(f"input name='{sess.get_inputs()[0].name}' and shape={sess.get_inputs()[0].shape}")
print(f"output name='{sess.get_outputs()[0].name}' and shape={sess.get_outputs()[0].shape}")
input name='float_input' and shape=[None, 4]
output name='output_label' and shape=[None]
We compute the predictions.
input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
label_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
import numpy # noqa: E402
pred_onx = sess.run([label_name], {input_name: X_test.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]
print(confusion_matrix(pred, pred_onx))
[[10 0 0]
[ 0 14 0]
[ 0 0 14]]
The prediction are perfectly identical.
Probabilities#
Probabilities are needed to compute other relevant metrics such as the ROC Curve. Let’s see how to get them first with scikit-learn.
prob_sklearn = clr.predict_proba(X_test)
print(prob_sklearn[:3])
[[4.93598913e-04 2.31913365e-01 7.67593036e-01]
[1.98141662e-02 8.74009455e-01 1.06176379e-01]
[2.21281673e-02 9.43041106e-01 3.48307262e-02]]
And then with ONNX Runtime. The probabilities appear to be
prob_name = sess.get_outputs()[1].name
prob_rt = sess.run([prob_name], {input_name: X_test.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]
import pprint # noqa: E402
pprint.pprint(prob_rt[0:3])
[{0: 0.0004935988690704107, 1: 0.23191338777542114, 2: 0.7675930261611938},
{0: 0.019814150407910347, 1: 0.8740096092224121, 2: 0.10617626458406448},
{0: 0.022128146141767502, 1: 0.9430410861968994, 2: 0.0348307266831398}]
Let’s benchmark.
from timeit import Timer # noqa: E402
def speed(inst, number=5, repeat=10):
timer = Timer(inst, globals=globals())
raw = numpy.array(timer.repeat(repeat, number=number))
ave = raw.sum() / len(raw) / number
mi, ma = raw.min() / number, raw.max() / number
print(f"Average {ave:1.3g} min={mi:1.3g} max={ma:1.3g}")
return ave
print("Execution time for clr.predict")
speed("clr.predict(X_test)")
print("Execution time for ONNX Runtime")
speed("sess.run([label_name], {input_name: X_test.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]")
Execution time for clr.predict
Average 6.08e-05 min=5.54e-05 max=8.58e-05
Execution time for ONNX Runtime
Average 2.26e-05 min=2.12e-05 max=2.89e-05
2.2578239968424898e-05
Let’s benchmark a scenario similar to what a webservice experiences: the model has to do one prediction at a time as opposed to a batch of prediction.
def loop(X_test, fct, n=None):
nrow = X_test.shape[0]
if n is None:
n = nrow
for i in range(n):
im = i % nrow
fct(X_test[im : im + 1])
print("Execution time for clr.predict")
speed("loop(X_test, clr.predict, 50)")
def sess_predict(x):
return sess.run([label_name], {input_name: x.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]
print("Execution time for sess_predict")
speed("loop(X_test, sess_predict, 50)")
Execution time for clr.predict
Average 0.00229 min=0.00188 max=0.00289
Execution time for sess_predict
Average 0.000358 min=0.000351 max=0.000386
0.00035805883999273647
Let’s do the same for the probabilities.
print("Execution time for predict_proba")
speed("loop(X_test, clr.predict_proba, 50)")
def sess_predict_proba(x):
return sess.run([prob_name], {input_name: x.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]
print("Execution time for sess_predict_proba")
speed("loop(X_test, sess_predict_proba, 50)")
Execution time for predict_proba
Average 0.00253 min=0.00249 max=0.00259
Execution time for sess_predict_proba
Average 0.000361 min=0.000355 max=0.000386
0.0003613862600468565
This second comparison is better as ONNX Runtime, in this experience, computes the label and the probabilities in every case.
Benchmark with RandomForest#
We first train and save a model in ONNX format.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier # noqa: E402
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10)
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
initial_type = [("float_input", FloatTensorType([1, 4]))]
onx = convert_sklearn(rf, initial_types=initial_type)
with open("rf_iris.onnx", "wb") as f:
f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
We compare.
sess = rt.InferenceSession("rf_iris.onnx", providers=rt.get_available_providers())
def sess_predict_proba_rf(x):
return sess.run([prob_name], {input_name: x.astype(numpy.float32)})[0]
print("Execution time for predict_proba")
speed("loop(X_test, rf.predict_proba, 50)")
print("Execution time for sess_predict_proba")
speed("loop(X_test, sess_predict_proba_rf, 50)")
Execution time for predict_proba
Average 0.0188 min=0.0184 max=0.0213
Execution time for sess_predict_proba
Average 0.000353 min=0.000347 max=0.00039
0.00035318371999892406
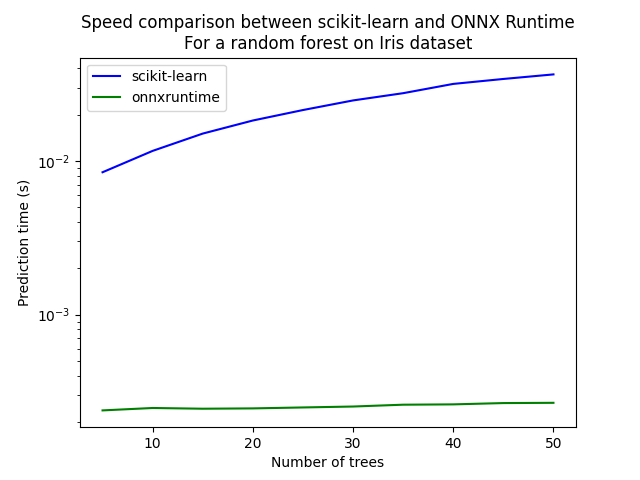
Let’s see with different number of trees.
measures = []
for n_trees in range(5, 51, 5):
print(n_trees)
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=n_trees)
rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
initial_type = [("float_input", FloatTensorType([1, 4]))]
onx = convert_sklearn(rf, initial_types=initial_type)
with open(f"rf_iris_{n_trees}.onnx", "wb") as f:
f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
sess = rt.InferenceSession(f"rf_iris_{n_trees}.onnx", providers=rt.get_available_providers())
def sess_predict_proba_loop(x):
return sess.run([prob_name], {input_name: x.astype(numpy.float32)})[0] # noqa: B023
tsk = speed("loop(X_test, rf.predict_proba, 25)", number=5, repeat=4)
trt = speed("loop(X_test, sess_predict_proba_loop, 25)", number=5, repeat=4)
measures.append({"n_trees": n_trees, "sklearn": tsk, "rt": trt})
from pandas import DataFrame # noqa: E402
df = DataFrame(measures)
ax = df.plot(x="n_trees", y="sklearn", label="scikit-learn", c="blue", logy=True)
df.plot(x="n_trees", y="rt", label="onnxruntime", ax=ax, c="green", logy=True)
ax.set_xlabel("Number of trees")
ax.set_ylabel("Prediction time (s)")
ax.set_title("Speed comparison between scikit-learn and ONNX Runtime\nFor a random forest on Iris dataset")
ax.legend()
5
Average 0.00692 min=0.00637 max=0.00846
Average 0.000185 min=0.000173 max=0.000209
10
Average 0.00985 min=0.00932 max=0.0113
Average 0.000184 min=0.000175 max=0.000207
15
Average 0.0127 min=0.0121 max=0.0143
Average 0.000186 min=0.000177 max=0.000206
20
Average 0.0154 min=0.0148 max=0.0169
Average 0.000189 min=0.000179 max=0.00021
25
Average 0.0181 min=0.0175 max=0.0196
Average 0.00019 min=0.00018 max=0.000217
30
Average 0.0209 min=0.0203 max=0.0226
Average 0.000189 min=0.000181 max=0.000211
35
Average 0.0234 min=0.0229 max=0.0251
Average 0.00019 min=0.000181 max=0.000216
40
Average 0.0262 min=0.0256 max=0.0279
Average 0.000195 min=0.000186 max=0.00022
45
Average 0.0292 min=0.0287 max=0.0308
Average 0.000195 min=0.000186 max=0.00022
50
Average 0.0316 min=0.0311 max=0.0331
Average 0.000199 min=0.000187 max=0.000232
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f701246c5b0>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.737 seconds)